

alias: GEO HAVILL, HARRY THORN
SNEAK, FORGER
Dagworth Hall as it looks todayAs I believe I’ve mentioned before, medieval chronicles are a gold mine for those of us who like our history to be laced with a bit of the bizarre. In between descriptions of wars, plagues, and other notable events, you are apt to suddenly find deadpan accounts of events that can be best described as barking mad. Ralph of Coggeshall was a monk in
More...
Strange Company - 6/30/2025
Wouldn’t you love to have interviewed Lizzie’s physician, Dr. Nomus S. Paige from Taunton, the jail doctor, ? He found her to be of sane mind and we can now confirm that he had Lizzie moved to the Wright’s quarters while she was so ill after her arraignment with bronchitis, tonsilitis and a heavy cold. We learn that she was not returned to her cell as he did not wish a relapse so close to her trial. Dr. Paige was a Dartmouth man, class of 1861. I have yet to produce a photo of him but stay tuned! His house is still standing at 74 Winthrop St, corner of Walnut in Taunton. He was married twice, with 2 children by his second wife Elizabeth Honora “Nora” Colby and they had 2 children,Katherine and Russell who both married and had families. Many of the Paiges are buried in Mount Pleasant Cemetery in Taunton. Dr. Paige died in April of 1919- I bet he had plenty of stories to tell about his famous patient in 1893!! He was a popular Taunton doctor at Morton Hospital and had a distinguished career. Dr. Paige refuted the story that Lizzie was losing her mind being incarcerated at the jail, a story which was appearing in national newspapers just before the trial. Mt. Pleasant Cemetery, Taunton, courtesy of Find A Grave. 74 Winthrop St., corner of Walnut, home of Dr. Paige, courtesy of Google Maps Obituary for Dr. Paige, Boston Globe April 17, 1919
More...
Lizzie Borden: Warps and Wefts - 5/24/2025
How did New Yorkers get through sweltering summer days before the invention and widespread use of air conditioning? Well, a lot of it depended on your income bracket. If you were wealthy, you likely waited out the summer at a seaside resort like Newport or on a country estate cooled by mountains or river breezes. […]
More...
Ephemeral New York - 6/30/2025
Youth With Executioner by Nuremberg native Albrecht Dürer … although it’s dated to 1493, which was during a period of several years when Dürer worked abroad. November 13 [1617]. Burnt alive here a miller of Manberna, who however was lately … Continue reading
More...
Executed Today - 11/13/2020
A boatman working near the foot of Little Street in
Brooklyn, on October 3, 1864, saw a package floating on the water. Thinking it
might contain something of value, he took it into his boat. He unraveled the enameled
oilcloth surrounding the package, and inside, covered in sheets of brown paper, was
the trunk of a human body. The head, arms, pelvis, and legs had been cut off
with a saw or sharp
More...
Murder By Gaslight - 6/28/2025
Soapy Smith STAR NotebookPage 20 - Original copy1884Courtesy of Geri Murphy(Click image to enlarge)
oapy Smith's early empire growth in Denver.Operating the prize package soap sell racket in 1884.
This is page 20, the continuation of page 19, and dated May 6 - May 29, 1884, as well as the continuation of pages 18-19, the beginning of Soapy Smith's criminal empire building in Denver, Colorado.&
More...
Soapy Smith's Soap Box - 6/1/2025
[Editor’s note: Guest writer, Peter Dickson, lives in West Sussex, England and has been working with microfilm copies of The Duncan Campbell Papers from the State Library of NSW, Sydney, Australia. The following are some of his analyses of what he has discovered from reading these papers. Dickson has contributed many transcriptions to the Jamaica […]
More...









 Mordecai Manuel Noah
Mordecai Manuel Noah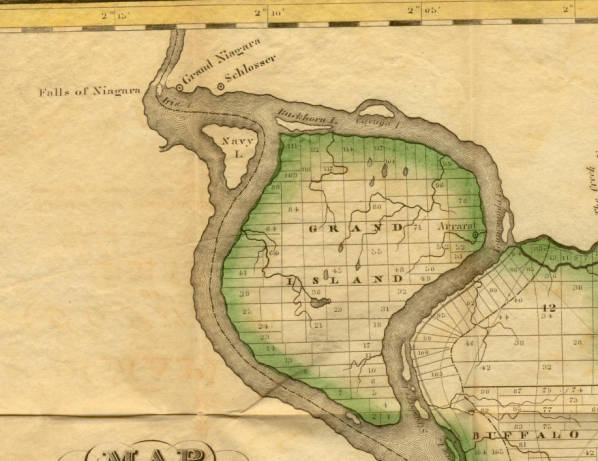 Grand Island, New York
Grand Island, New York



